Ingredients and Their Nutritional Contributions
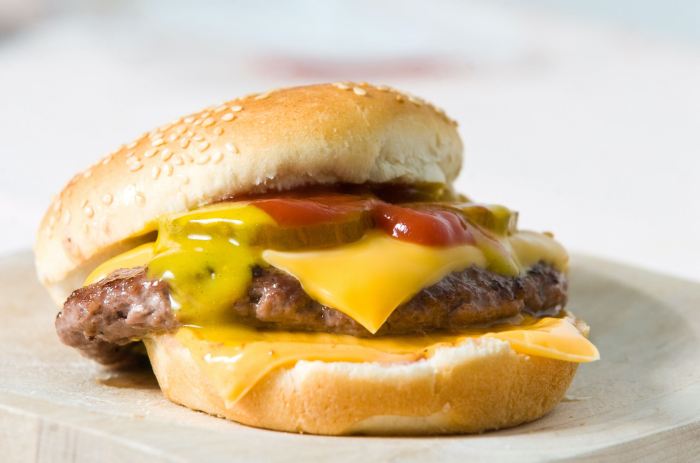

Quarter pounder nutrition facts – Understanding the nutritional profile of a Quarter Pounder requires examining its constituent ingredients and their individual contributions. The nutritional value is a complex interplay of fats, proteins, carbohydrates, and various micronutrients, all influenced by sourcing and processing methods.
The Quarter Pounder’s nutritional profile is largely determined by its core ingredients: the beef patty, bun, cheese, and additions like ketchup, mustard, and pickles. Each component plays a distinct role in the overall nutritional composition, both positively and negatively impacting its overall value.
Understanding the nutritional content of a Quarter Pounder is crucial for mindful eating. Many consider pairing it with a beverage, and often the choice falls on Diet Coke; you can find detailed information on diet coke nutrition facts to make an informed decision. Returning to the Quarter Pounder, it’s important to remember that its high fat and calorie content should be balanced within your overall daily intake.
Main Ingredients and Their Nutritional Impact
The following list details the key ingredients of a Quarter Pounder and their respective nutritional contributions. Note that exact values can vary slightly depending on preparation methods and supplier specifications.
- Beef Patty (approximately 4 ounces): Provides a significant source of protein, essential for building and repairing tissues. However, it also contributes a substantial amount of saturated fat, which can negatively impact cardiovascular health if consumed excessively. The leanness of the beef and the cooking method significantly influence the final fat content. Grass-fed beef, for example, generally has a more favorable fatty acid profile than grain-fed beef.
- Bun: Primarily composed of refined carbohydrates, providing quick energy but lacking significant micronutrients. The bun also contributes to the overall calorie and carbohydrate count of the sandwich. The type of flour used (e.g., white versus whole wheat) affects the nutritional profile, with whole wheat offering more fiber and nutrients.
- Cheese (typically American cheese): Adds fat and protein, along with some calcium and other micronutrients. However, it also contributes to the overall sodium and saturated fat content. Different types of cheese will offer varying nutritional profiles, with some being higher in fat and sodium than others.
- Ketchup, Mustard, Pickles: These condiments add minimal nutritional value but contribute to the overall sodium content. The quantities used influence their impact, with larger amounts increasing sodium intake.
Impact of Ingredient Sourcing and Processing
The sourcing and processing of ingredients significantly influence the final nutritional profile of a Quarter Pounder. For example, the type of beef used (grass-fed vs. grain-fed), the type of bun (white vs. whole wheat), and the cheese variety all affect the fat content, micronutrient density, and overall caloric value. Processing methods, such as the use of additives or preservatives in the bun or cheese, can also impact the nutritional quality.
Similarly, the cooking method for the patty influences its fat content and the formation of potential harmful compounds.
Combined Nutritional Effect of Ingredients, Quarter pounder nutrition facts
The combination of these ingredients results in a Quarter Pounder that is relatively high in calories, fat (particularly saturated fat), and sodium. While it provides protein, it is often low in fiber and other essential micronutrients. The overall nutritional value is therefore considered less than optimal for regular consumption as part of a balanced diet, particularly due to the high saturated fat and sodium content.
The significant calorie count contributes to potential weight gain if consumed frequently without adequate physical activity and overall dietary balance. Choosing leaner beef options, whole-wheat buns, and reduced-sodium condiments can slightly improve the nutritional profile, but the overall impact remains substantial.
Dietary Considerations and Recommendations

A Quarter Pounder, while undeniably delicious, presents a significant nutritional profile that requires careful consideration within the context of various dietary needs and health goals. Understanding its composition and potential impact on different diets is crucial for making informed choices about its consumption. This section explores the suitability of a Quarter Pounder for specific dietary patterns, offers suggestions for healthier modifications, and highlights potential health consequences associated with regular intake.
Suitability for Different Diets
The Quarter Pounder’s high fat, moderate protein, and relatively high carbohydrate content makes it unsuitable for many restrictive diets. For individuals following a low-fat diet, the significant amount of saturated fat from the beef patty and cheese is a major concern. Similarly, those on a low-carbohydrate diet will find the bun and potentially added sauces contribute a substantial amount of carbohydrates.
High-protein diets may find the protein content adequate, but the high fat content could still be problematic depending on the specific macronutrient targets. In summary, the Quarter Pounder is not a good fit for individuals strictly adhering to low-fat or low-carbohydrate diets.
Modifying a Quarter Pounder for Healthier Consumption
Several modifications can be made to improve the nutritional profile of a Quarter Pounder. Choosing a whole-wheat bun instead of a regular bun can increase fiber intake. Removing cheese will significantly reduce saturated fat and calories. Requesting fewer sauces, or opting for lighter options like ketchup instead of mayonnaise, can also contribute to a healthier version. Replacing the beef patty with a grilled chicken or veggie patty provides a lower-fat and potentially higher-protein alternative, depending on the specific product.
These changes can lessen the negative health impacts associated with the standard Quarter Pounder.
Potential Health Consequences of Regular Consumption
Regular consumption of Quarter Pounders, due to their high saturated fat, sodium, and calorie content, can contribute to several health problems. High saturated fat intake is linked to increased cholesterol levels and a heightened risk of cardiovascular disease. The high sodium content can contribute to high blood pressure. The high calorie density can lead to weight gain and obesity, which are risk factors for numerous health issues including type 2 diabetes and certain cancers.
For example, consistently choosing a Quarter Pounder as a regular meal option, instead of a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein, can significantly increase the risk of these health problems over time. Therefore, moderation is key.
General Inquiries: Quarter Pounder Nutrition Facts
What are the best substitutions to make a Quarter Pounder healthier?
Opt for lettuce wraps instead of the bun, request no cheese or mayonnaise, and choose a lighter sauce like ketchup or mustard.
How does the Quarter Pounder compare to a veggie burger in terms of nutrition?
Veggie burgers generally have fewer calories and less fat than a Quarter Pounder, but protein content can vary. Nutritional values differ significantly depending on the specific brand and ingredients of the veggie burger.
Does grilling a Quarter Pounder affect its nutritional content?
Grilling can slightly reduce the fat content as some fat may drip off during cooking, but the overall nutritional impact is minimal.
Are there any specific health risks associated with frequent Quarter Pounder consumption?
Regular consumption of high-calorie, high-fat foods like the Quarter Pounder can contribute to weight gain, increased cholesterol levels, and an elevated risk of heart disease if not part of a balanced overall diet.